- Published on
PC Power Supplies (Part 1)
- Authors
- Name
- Sam Mark
- @Twitter/smmk

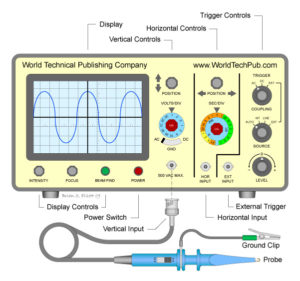
The Power supply is a humble, unassuming, but important part of a modern computer. Why do modern PC even need a power supply? what does it do? How do i pick the right one? Electricity travels in pulses we represent those pulses in waves. Modern computers need very stable and predictable waveforms. You can imagine how hard it would be to operate a processor at 3 gigahertz or 3 billion cycles per second if you electric supply is unsteady. You can visualize theses waves with an electrical monitoring tool called a oscilloscope.
PC power supplies are important because the power we get from the wall in the United States is 120V AC and 60 Hertz. The alternating current electricity we get from the wall is flips its polarity at 60 times a seconds. The first alternating current motor was invented by Nikola Tesla. This also means he invented the alternating current generator. This is great because AC electricity travels over long distances very well. It is also very efficient at powering AC motors because it is generated by AC Generators.
The power we get if often affected by fluctuations in the grid supply, from things like winds, power transformer failures, fallen power poles, and lighting etc. PC only use DC or direct current. This means a power supply needs a good rectifier, and filter that can take in the noisy fluctuating power from the wall and convert it to Direct Current electricity. DC power doesn’t change polarity but does travel in wave form. PC often use powerful transformers to output DC electricity at 3.3, 5, and 12 volts of DC power. Many power supplies use a switching controller to make sure that these voltages are supplies with very little fluctuations.
The most important number is the overall power the power supply can well supply to the PC components theses it of often represented by unit watts. A watt is a unit of measurement that represents 1 joule per second. For PC that means its a limit to how much power can be supplied to a computer. Every component will draw a certain wattage from the power supply. CPUs can draw anywhere from 40-150 watts; Motherboards can draw 25-80 watts; Ram anywhere from 2-6 watts; hard drives SSDs 1-3 watts, HDDs 7-10 watts each; videos cards often the most power hungry can vary from 25-400 watts. All you have to do is look up the wattage and add it all together to find the power supply wattage you need. Typically PC power supplies come in 500 -1000 wattage ranges, but there are outlier if you building a really low wattage or very high wattage computer. You typically want to add around 100 watts overhead to your total so you don’t underrate your system. You can buy a power supply that supplies a lot more power then your system needs with no ill effects to you system, but it will effect your wallet. But what you do not want to do is underrate your system. If you do you can suffer some bad effects to your computer like random power-outs, not turning on at all and every blowing up your power supply.
There are also other considerations when buying power supplies i will put this all in another blog entry.